Definition and Function:
Differential pressure transmitter is an industrial automation instrument used to convert pressure difference signals into standard signals, achieving precise monitoring and control of industrial fluid pressure, flow rate, liquid level and other parameters.

Working principle:
It contains high-precision pressure sensors (such as capacitive, diffused silicon, etc.) inside. Taking capacitive as an example, the pressure difference causes the elastic diaphragm to deform and change the capacitance value. After circuit and algorithm conversion, it is output as standard signals such as 4-20mA current or 0-5V voltage.
Working principle of differential pressure transmitter:
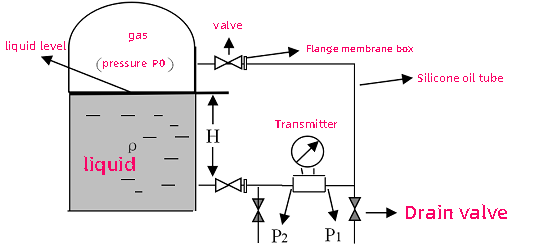
Classification:
According to the principle: capacitive, diffused silicon, vibrating wire (high stability), piezoelectric (suitable for high-frequency dynamic measurement).
According to structure and scenario: ordinary type; Isolation type (anti-corrosion, anti blocking, used in chemical industry, etc.); Remote transmission type (solving measurement difficulties in special environments).
Application field:
Petrochemical industry (flow measurement, liquid level); Electricity (monitoring boiler water level, turbine vacuum degree); Wastewater treatment (measuring sludge concentration); Measurement of production parameters in industries such as food and beverage, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals.
Advantages:
High measurement accuracy (within ± 0.1% of partial error); Strong stability (adaptable to harsh environments); Good compatibility (easy to integrate automation control); Compact structure, easy installation and maintenance.
Challenges faced:
measuring impurities, high viscosity media that can easily block pipelines, and contaminating sensors; Strong electromagnetic interference affects signal transmission; Need to meet the requirements of intelligence and multifunctionality.
Development trend:
Intelligence (Internet of Things, fault warning); high-precision; miniaturization; Networking (device interconnection).
